- Proximal stripping
- Arch expansion
- Distalizationof molars
- Uprightingof tilted teeth
- Derotationof posterior teeth
- Proclinationof anterior teeth
- Extraction
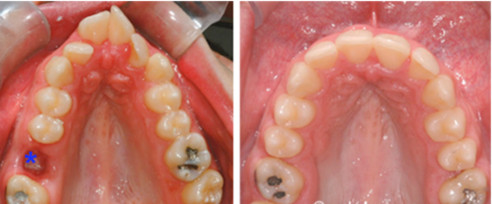
Proximal stripping
lnterproximal reduction (IPR), also known as “tooth stripping” or “interdental reduction,” is the removal of small amounts of outer enamel tooth surface between two adjacent teeth. This is beneficial when a small amount of dental crowding must be eliminated and the removal of adult teeth or expansion of the dental arches by themselves are not the best option. In other words, it is a means to acquire additional space to create ideal tooth alignment.
Arch expansion
Rapid palatal expansion is a preliminary treatment procedure that aims at enlarging the maxillary dental arch and the palate (roof of the mouth) to re-establish balance between the width of the jaws. This procedure is also called “maxillary expansion”.
Distalizationof molars
Molar distalization is a process in the field of Orthodontics which is used to move molar teeth, especially permanent first molars, distally (backwards) in an arch. This procedure is often used in treatment of patients who have Class 2 malocclusion. The cause is often the result of loss of E space in an arch due to early loss of primary molar teeth and mesial (forward) migration of the molar teeth. Sometimes molars are distalized to make space for other impacted teeth, such as premolars or canines, in the mouth.
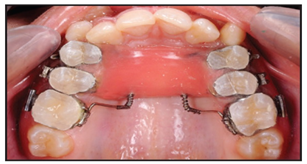
Distalization in the maxillary arch is easier than the mandibular arch because maxillary bone has more trabecular bone than the mandible, which has higher percentage of cortical bone.
Uperightning of posterior teeth
A tipped mandibular molar is a frequent situation among orthodontic patients, which usually occurs after premature loss of adjacent teeth leading to the inclination of the molars . However, molaruprighting into its correct position leads to the normalization of the functional and periodontal condition
Derotation of posterior teeth
If a patient regularly visits the dental clinic, the dentist can closely monitor these cases both clinically and radiographically, so that the etiology of these malocclusions can be detected and these problems can be intercepted at an early age (interceptive orthodontics) when the case is referred to the consultant orthodontist.
In cases where the patient is a teenager or an adult patient presenting rotations visiting the orthodontic clinic, they are treated as routine orthodontic cases. These cases require extensive biomechanics and do have a tendency to relapse if proper retention techniques are not followed.
Force required for derotation is variable from case to case.
Mostly, these cases are treated as routine orthodontic cases as there is very little awareness about these problems among patients, and they don’t realise the importance of interceptive dental treatment.
Proclination of anterior teeth
Proclinationof anterior teeth can be undertaken incases where these teeth are retroclinedor their proclinationwill not effect the soft tissue profile orthe stability of the results.Any of the procliningmsprings (‘Z’ spring, mattressspring) or screws (medium-, mini-, or micro-screws) or fixed appliances can be used for the purpose.
Extraction
Painless removal of teeth from its socket istermed as Extraction.
It is one of the most common methods ofgaining space in the arch.